查询执行器优化点
多机执行模型
多核执行模型
单核执行模型
SIMD
多核并行优化点
C++ Low Level
列式布局
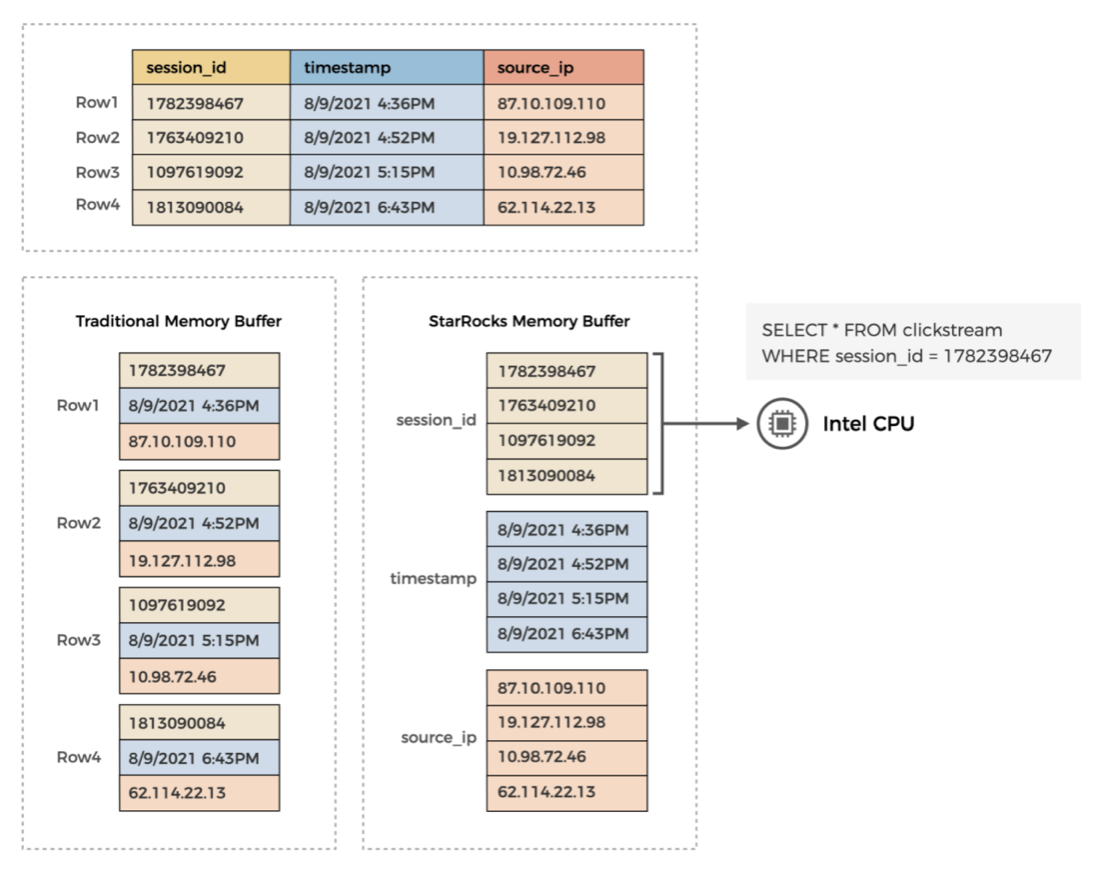
Batch 操作
按列处理
- 更少的虚函数调用
- 更少的分支判断
- CPU Cache 更友好
- 易于SIMD优化
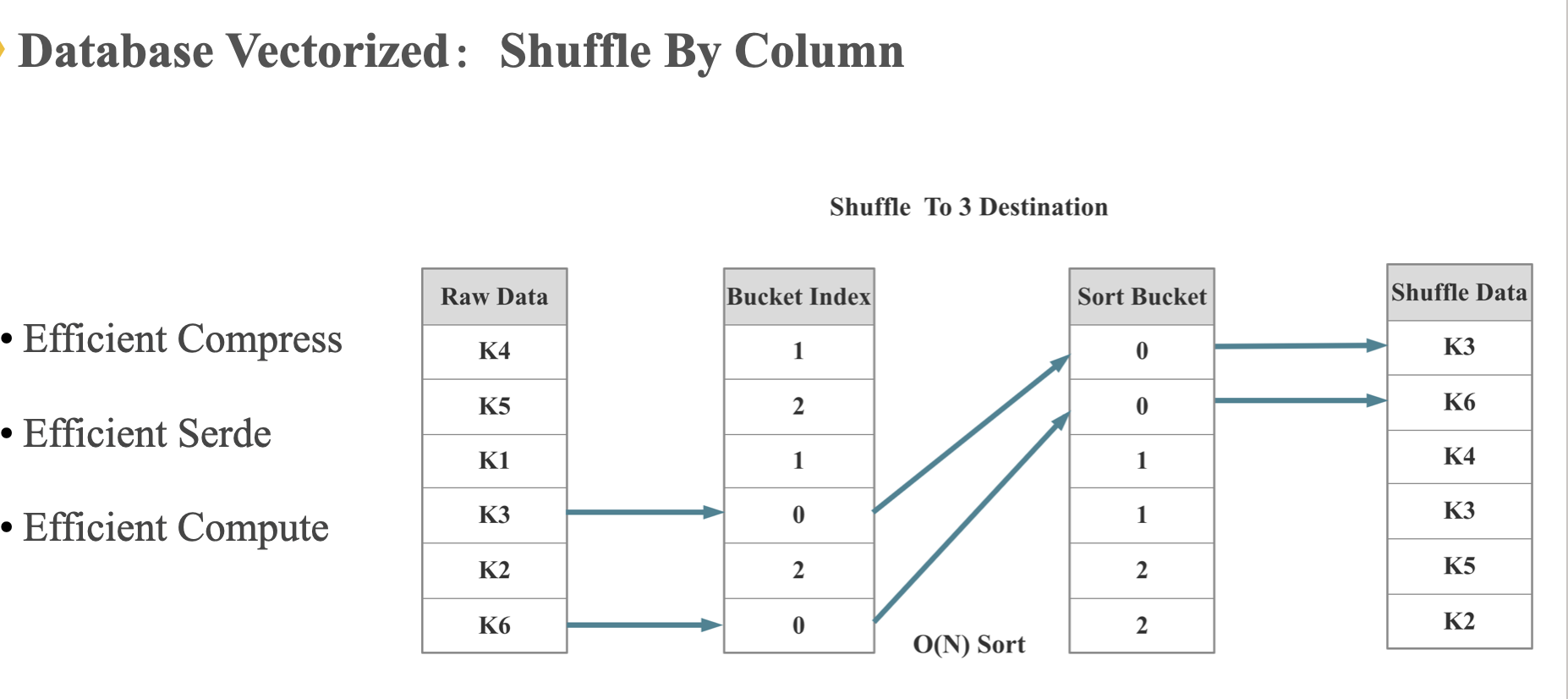
Shuffle By Column
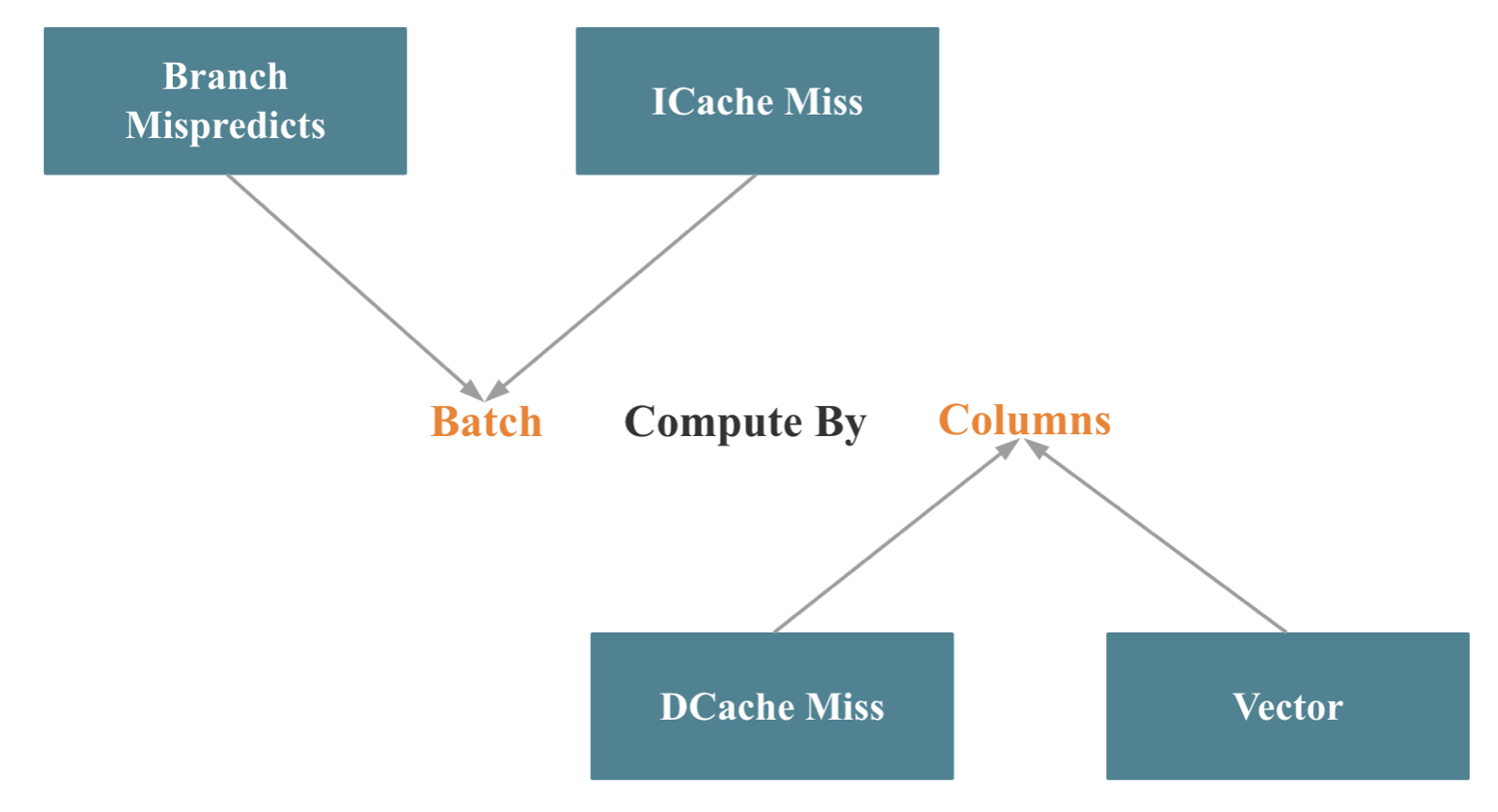
虚函数调用
分支预测
5星力荐的视频教程: Branchless Programming in C++ - Fedor Pikus - CppCon 2021
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-WPhYREFjk
分支预测的原理,以及在实际代码中的优化点都讲的很清楚
对应的 PPT 文件:
https://github.com/CppCon/CppCon2021/blob/main/Presentations/Branchless_computing.pdf
分支取直(Branch Straightening)
整数区间判断
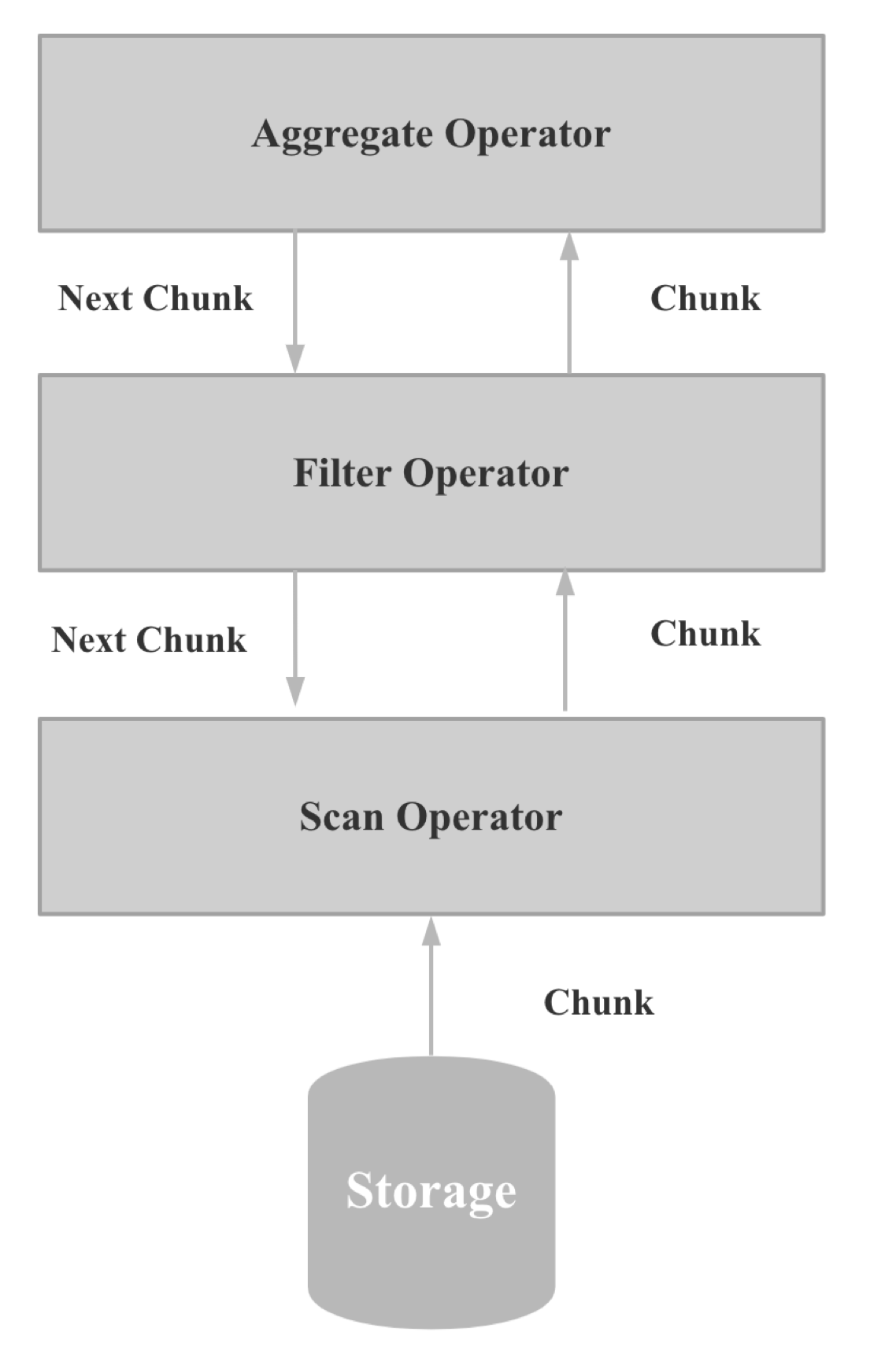
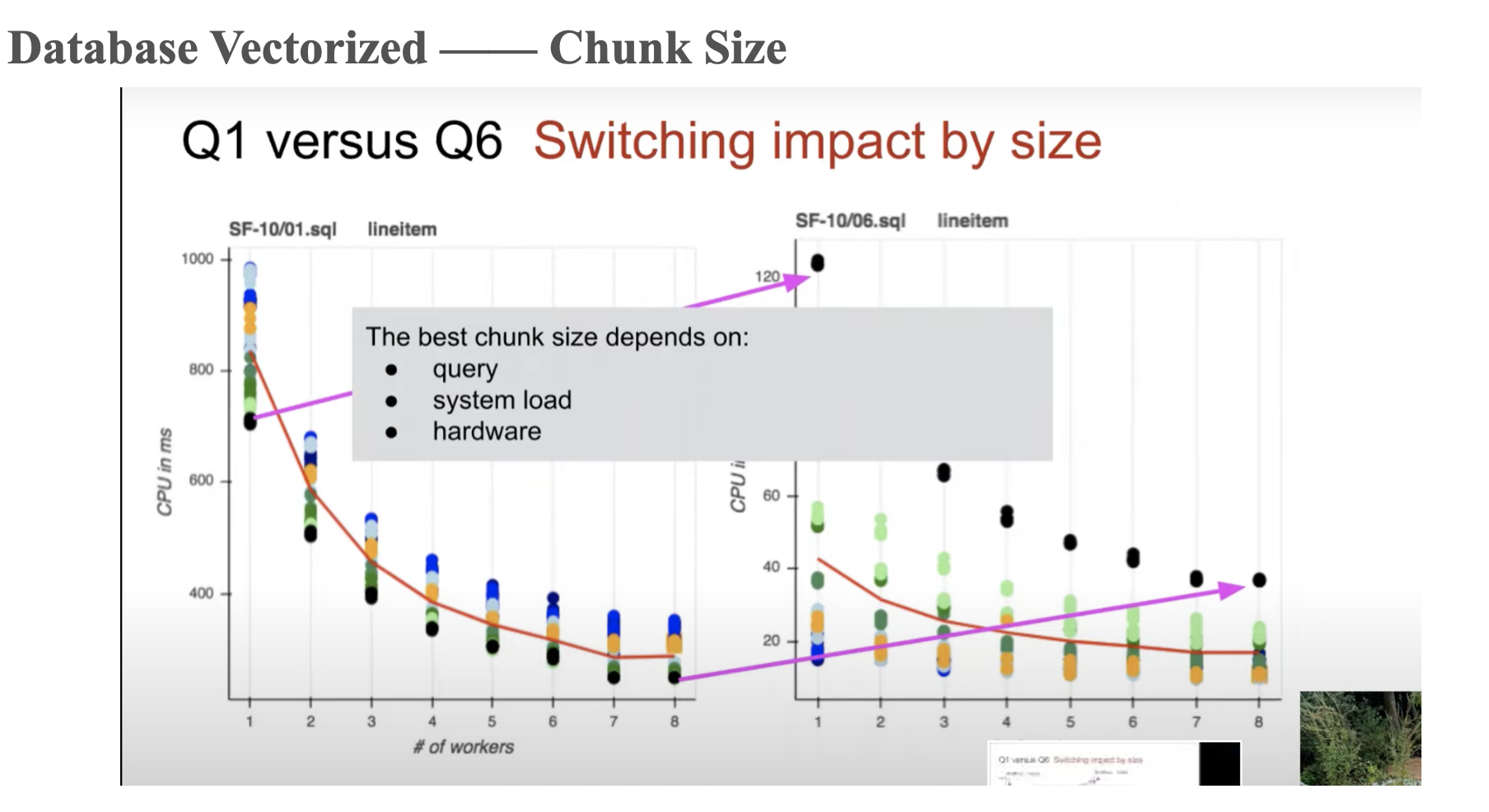
Chunk Size
Query Cache
CPU Cache 优化
pack data,尽可能 touch 足够小的内存
Cache-line Misses 的惩罚
- 失效次数增多:当一个缓存行失效时,需要从主存中加载新的数据块到缓存中,这会导致额外的内存访问开销。如果有大量的缓存行失效发生,会导致频繁的内存访问,增加了系统的总体延迟。
- 惩罚更大:当多个处理器核心同时访问相同的缓存行时,会发生缓存行竞争(cache-line contention)。如果某个核心修改了缓存行中的数据,并且其他核心也需要访问相同的缓存行,那么缓存一致性协议(如MESI)将会导致其他核心失效它们的本地缓存行,重新从主存加载。这种竞争和冲突会增加延迟,并降低多核系统的整体性能。
内存布局
Improve Locality (Spatial And Temporal)
时间局部性:Reduce cache miss when evaluate lots of expr in aggregate https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/pull/15998
Align The Code And Data
Reduce Memory Footprint
Block
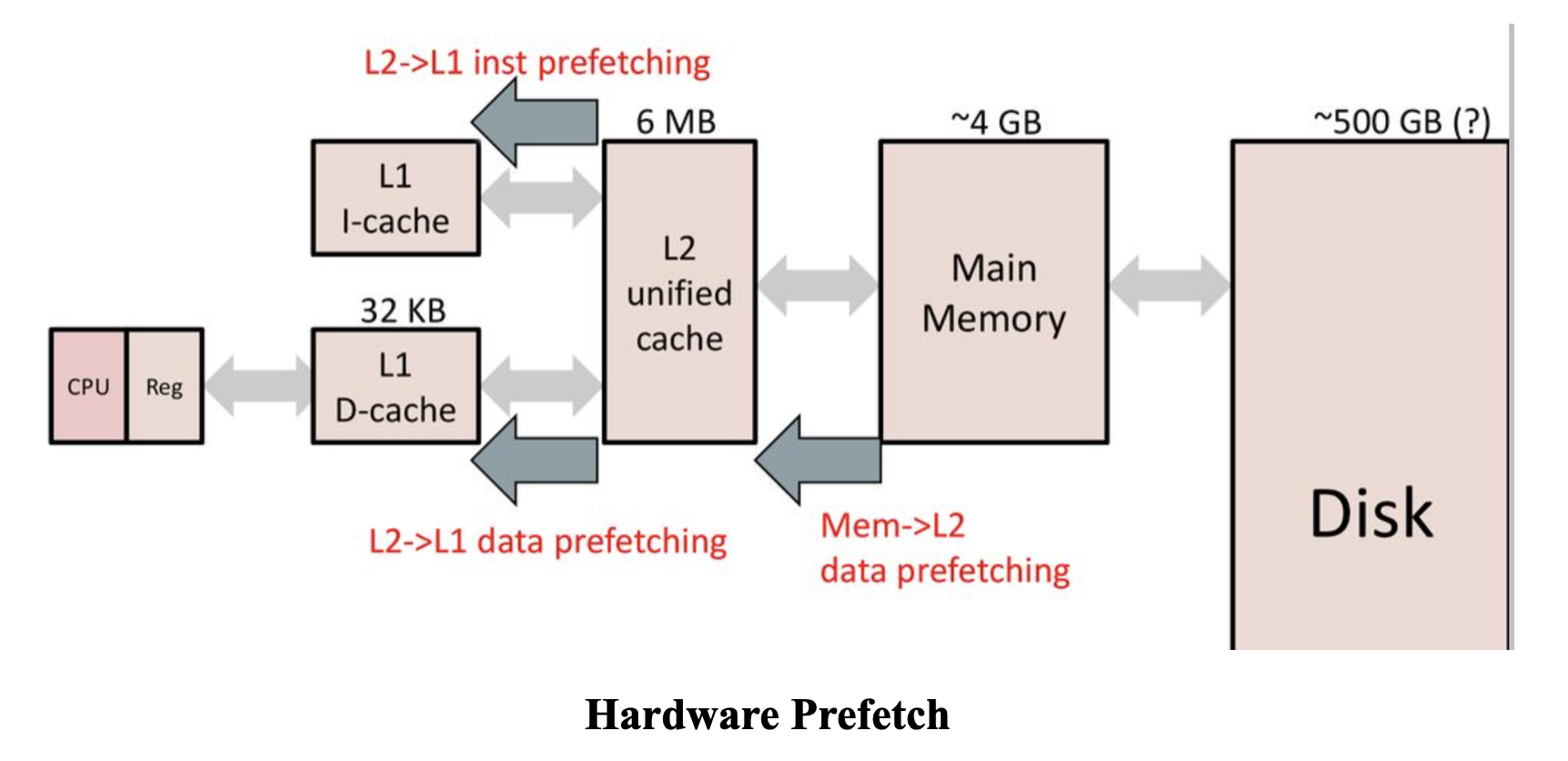
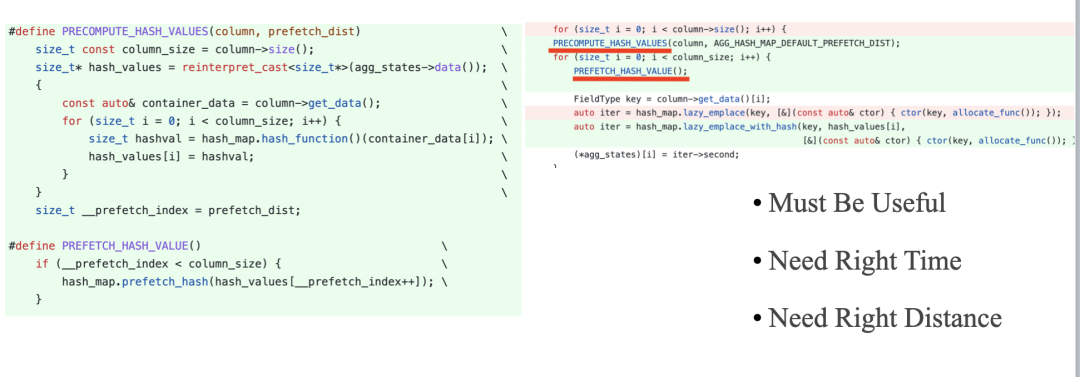
Prefetch
Hardware Prefetch
Software Prefetch
Code Cache
优化实例:
https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/pull/23300
避免多级指针检索
多级指针检索可能导致 Cache Miss 的原因如下:
数据局部性破坏:多级指针访问通常涉及间接引用,需要多次内存访问才能到达目标数据。这会导致数据的局部性破坏,即访问的数据位置不连续,无法充分利用缓存中已加载的数据块。
缓存行填充:缓存以缓存行(Cache Line)为单位进行数据加载。当多级指针访问的数据存储在不同的缓存行中时,每次访问都可能引发缓存行填充,即需要从主存中加载整个缓存行,即使只需要访问其中的一小部分数据。
指针跳跃:多级指针访问可能涉及不同层级的指针跳跃,即在不同的内存地址之间跳转。这会导致缓存中的预取机制失效,无法准确预测后续的内存访问模式,从而增加了缓存失效的可能性。
Pointer-chasing(指针追踪)
Pointer-chasing(指针追踪)是指在计算过程中频繁地通过指针访问和跳转到其他内存位置的操作。这种操作通常出现在数据结构中,其中一个对象的属性或元素是指向另一个对象的指针。指针追踪的过程可以涉及多次内存访问和跳转,可能会对性能产生影响
影响性能的因素包括以下几点:
内存访问延迟:指针追踪涉及多次内存访问,每次访问都可能引入内存访问延迟。当指针跳转到新的内存位置时,可能需要从主存中加载数据,这会导致较长的访问延迟,降低性能。
CPU 缓存效果:指针追踪操作可能导致缓存不命中(cache miss)。当指针跳转到新的内存位置时,新的内存位置可能不在 CPU 缓存中,需要从内存中获取数据,这会增加访问时间。频繁的指针追踪操作可能导致较高的缓存不命中率,降低 CPU 缓存效果,进而降低性能。
频繁的分支预测错误:指针追踪操作可能导致频繁的分支预测错误。当指针跳转到不同的内存位置时,可能会触发分支语句,而分支预测错误会引入额外的开销。高度依赖指针追踪的代码可能会导致较高的分支预测错误率,降低性能。
HashTable 优化
表达式
Const 优化
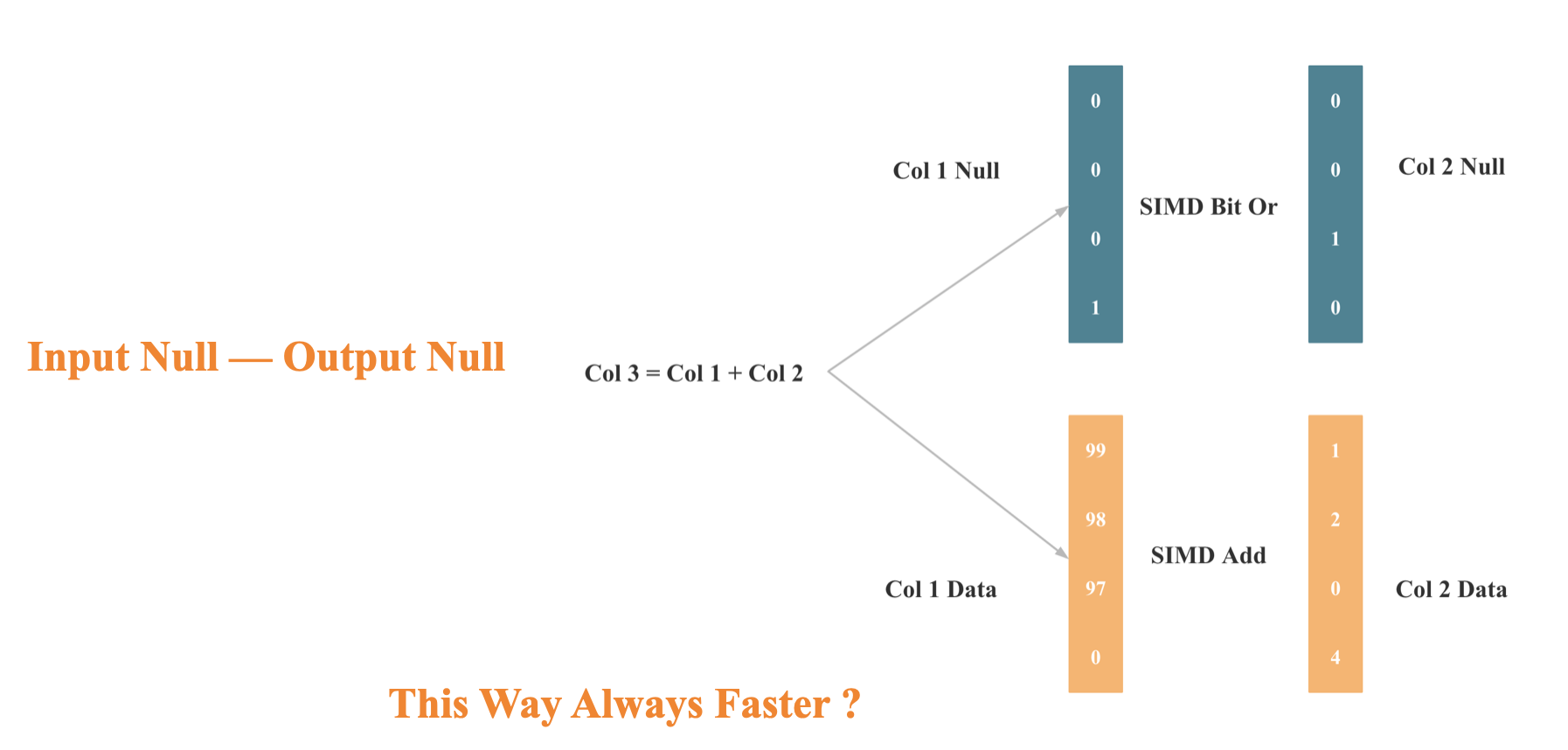
Null 优化
Runtime Filter
What Is Runtime Filter
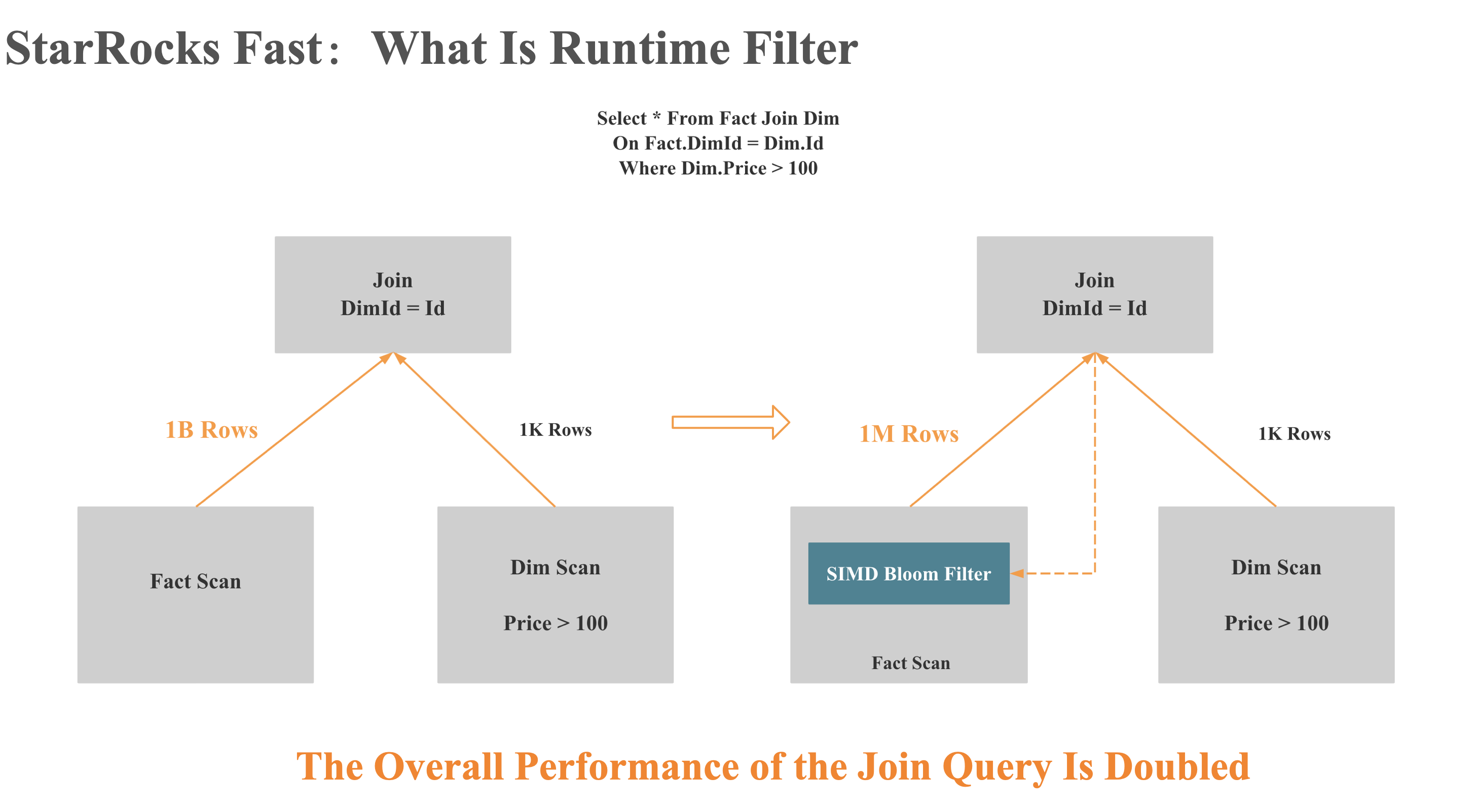
Runtime Filter 的意义
- Reduce Scan Disk IO
- Reduce Network Transport
- Reduce Join Probe Rows
越复杂的 Join SQL,数据量越大的数据集,Runtime Filter 的优化意义越大, Runtime Filter 带来 10倍到 100倍的性能提升。 10 倍到 100倍 是 StarRocks 真实用户生产环境的数据。
Runtime Filter 的优化点
- Support Local And Global Runtime Filter
- Shuffle Aware
- Push down Max/Min, In Filter To Storage Engine
- Cost Estimation Based
- Support Runtime Filter Cache
- Push Runtime Filter To Two Sides
- SIMD Bloom Filter
- Adaptive Join Runtime Filters Selection
- Multi Column Runtime Filter
- 只下推有选择性的 Runtime Filer
Local Join Runtime Filter
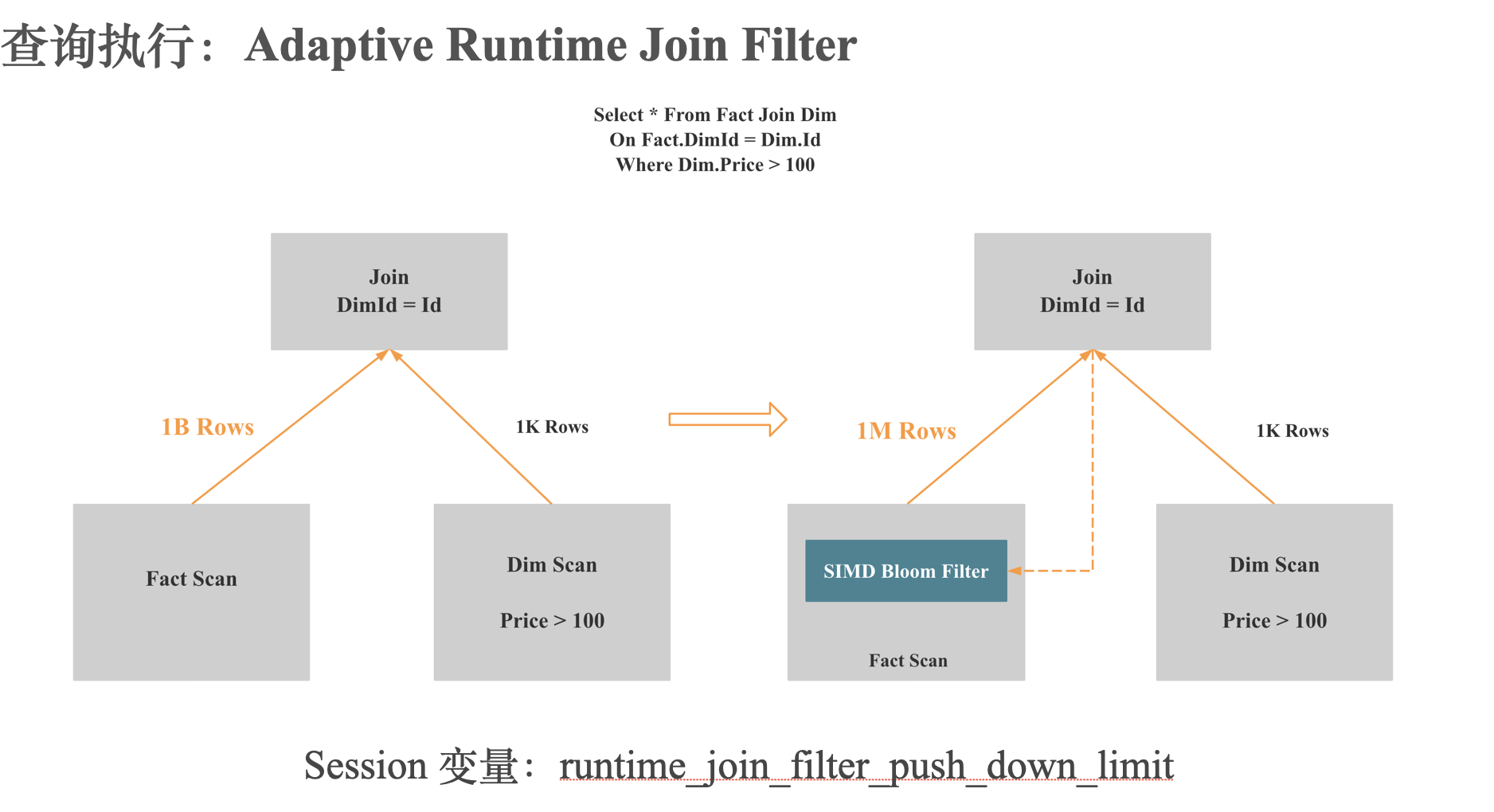
Global Join Runtime Filter
Top-N Runtime Filter
Runtime filter 是否 Merge
自适应 Scan wait time
自适应的 push down row limit
Decimal 乘法
IO 调度
全局低基数字典
网络传输
提前短路
Hash Join 提前短路
Limit 提前短路
内存管理 Memory Management
避免 Copy
内存分配的连续性
尽可能早的释放内存
内存复用
[Enhancement] Optimize the performance for regexp_replace
https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/pull/16356
Memory alignment
- Unaligned store instructions that straddle a cache line incur a bit of a performance penalty.
- Unaligned store instructions that straddle a page boundary are substantially slower (taking about 4x as long to execute).
- Unaligned store instructions that do not straddle either of these boundaries are almost free on modern CPU’s
Column Pool
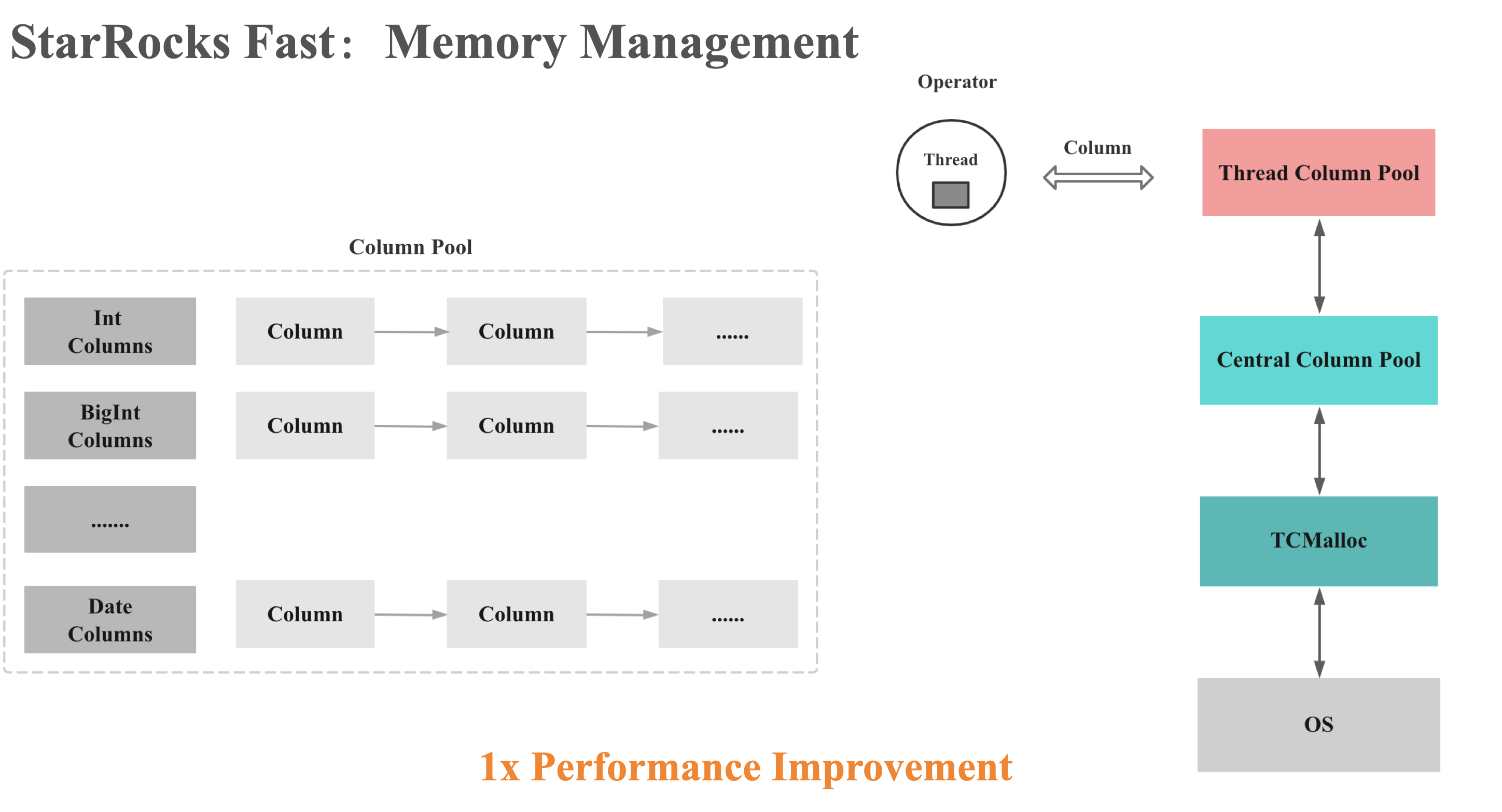
线程模型
序列化
Operations on Encoded Data
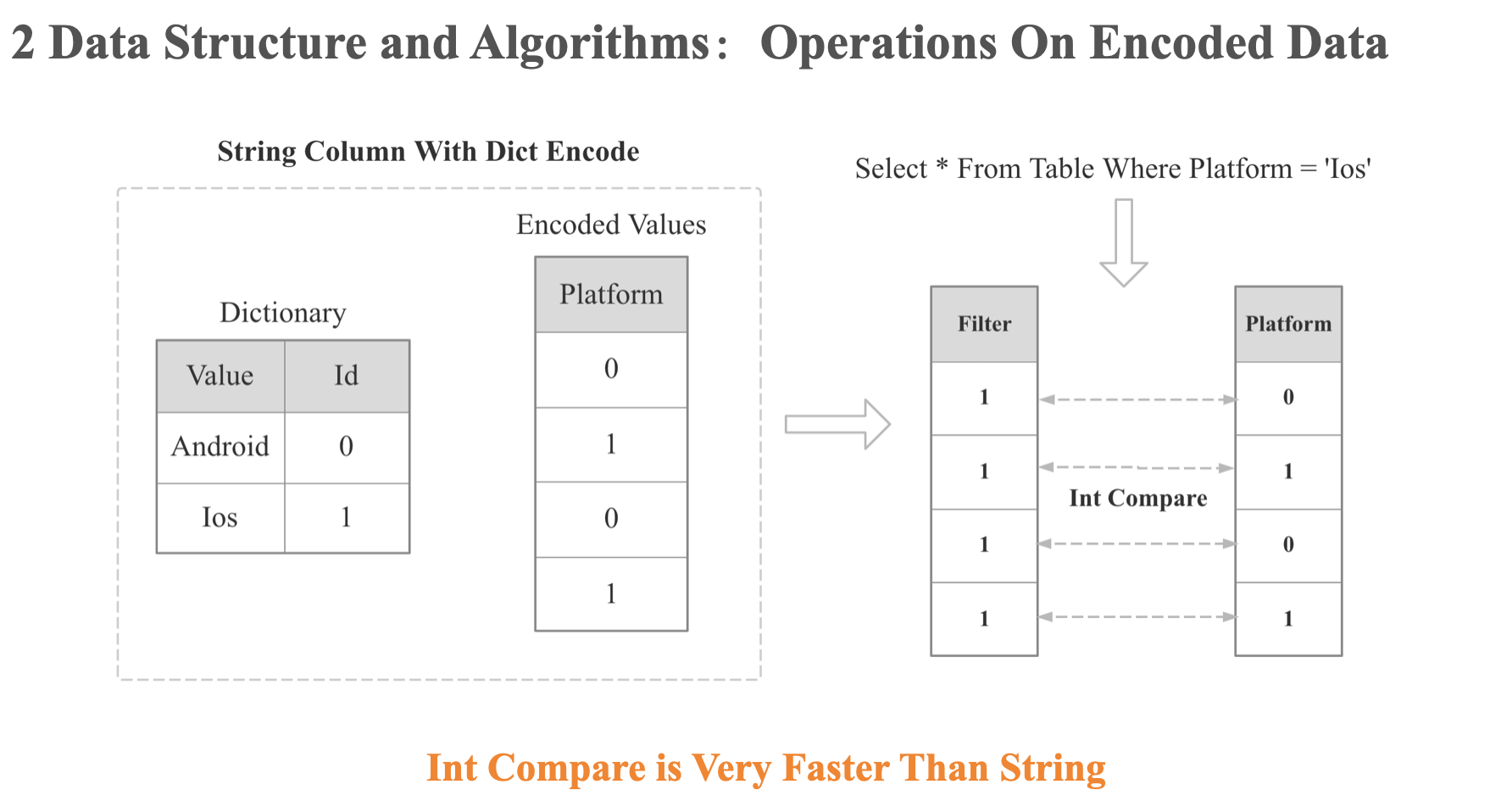
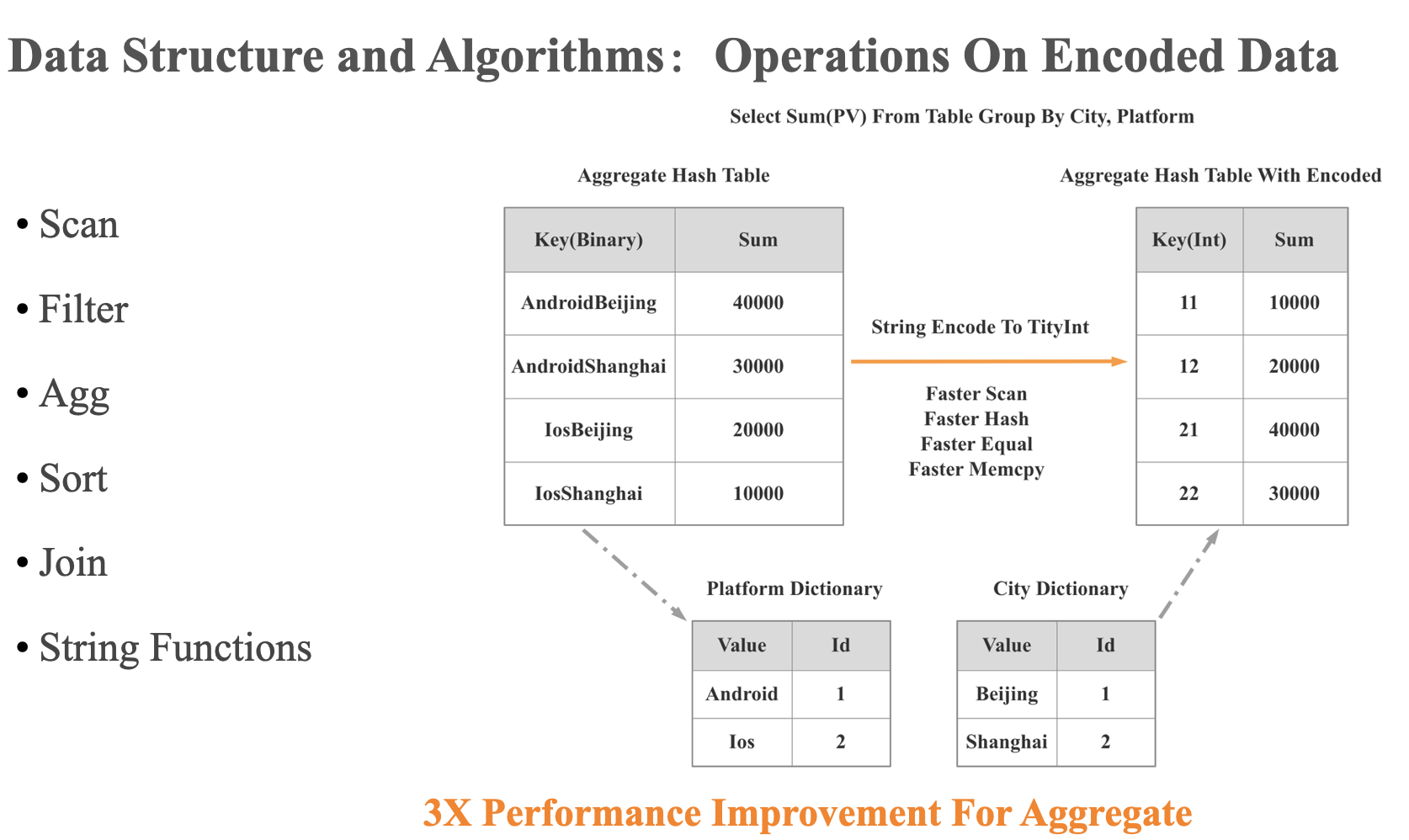
https://archived.docs.singlestore.com/v7.0/concepts/understanding-ops-on-encoded-data/
可以操作数据的编码方式:
- dictionary encoding
- run-length encoding
- integer value encoding
可以优化的算子:
- Scan
- Filter
- Group By
- Aggregate
- Expressions
- Join
- Sort
- Union
Code Gen
编译器优化
-O3 默认开启的性能编译选项
-finline-functions
-ftree-loop-vectorize
-ftree-slp-vectorize
-funswitch-loops
-ftree-loop-distribute-patterns
-ffast-math
Link-Time Optimization (LTO)
Profile-Guided Optimization (PGO)
代码布局
Link Order Changes function addresses
精确去重
异步
Adaptive
Adaptive Join Runtime Filters Selection

Adaptive Streaming Aggregate
Adaptive Aggregate Hash Map Selection
Adaptive IO 并发度
Adaptive Filter Execution Strategy
Adaptive Encoding
Adaptive Pipeline Parallelism
- BE CPU Core Number
- Query Type
- Data Size
- Operator Type
- Data Distribution
- Statistical Information
资料
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236345471_Adaptive_Query_Processing
循环相关优化
1:循环无关码外提——将循环内的某些无关代码外移,减少某些程序的反复执行 2:循环展开——减少循环条件的判断,针对循环次数少的循环 3:循环判断外提——减少每次循环的都进行判断次数 4:循环剥离——将不通用的处理起来稍微费劲一些的动作,放在循环外处理
循环交换(Loop Interchange)
内循环访问行,外循环访问列
